- Details
- Category: datasets
For further information about the dataset
Roberto Basili
Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia
Via di Vigna Murata, 605 - 00143 Roma, Italy
e-mail:
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1213-0828
For further information about the web services
Roberto Vallone
Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia
Via di Vigna Murata, 605 - 00143 Roma, Italy
e-mail:
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1208-9412
- Details
- Category: datasets
Global Dip (G-DIP): a collection of earthquake fault dip angles
G-DIP is a compilation of 597 uniquely determined fault plane dip angles corresponding to 269 individual earthquakes. It includes two main types of dip determinations: one based on the Global Centroid-Moment-Tensor Project (https://www.globalcmt.org/), the CMT collection, with 253 dip determinations of the activated nodal plane, and the other based on studies that used various techniques, the FLT collection, with 229 fault dip determinations. The FLT collection includes 525 cases of multiple determinations for the same earthquake. The paired determinations, i.e., earthquakes for which the CMT solution and at least one FLT solution exist, are 221. All determinations are classified depending on faulting categories as normal, reverse, transcurrent crustal faulting, and subduction-interface reverse faulting. Most of these earthquakes are located near plate boundaries; 63 are reverse faulting events identified as having occurred on subduction interfaces, 184 occurred in the continental crust, and 18 in the oceanic crust. Four subduction interface earthquakes were discarded because their faulting mechanism is inconsistent with reverse faulting. Among all the 202 crustal earthquakes, 68 events are located at a distance greater than 300 km from the plate boundaries. Several of these earthquakes that occurred in the plate interiors are located very far away from plate margins, such as those in the North American, Australian, and Asian continental interiors; one of them is in the middle of the Pacific plate. The transcurrent faulting earthquakes include both oceanic transforms and continental strike-slip faults. None of the normal faulting earthquakes belong to oceanic spreading ridges because of the lack of univocal fault plane determinations in that specific tectonic setting. Earthquakes classified as intraslab are not included.
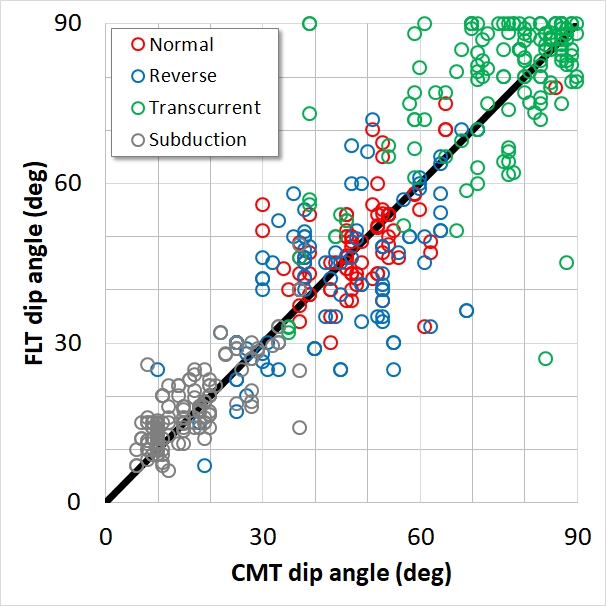
Dip angles of paired events from the CMT and FLT collections. The solid black line indicates the 1:1 ratio. The scatter of each faulting category estimated by the root mean squares is as follows: Normal RMS=0.153 rad (~9°); Reverse RMS=0.214 rad (~12°); Transcurrent RMS=0.227 rad (~13°); Subduction RMS=0.084 rad (~5°); all data together RMS=0.179 rad (~10°).
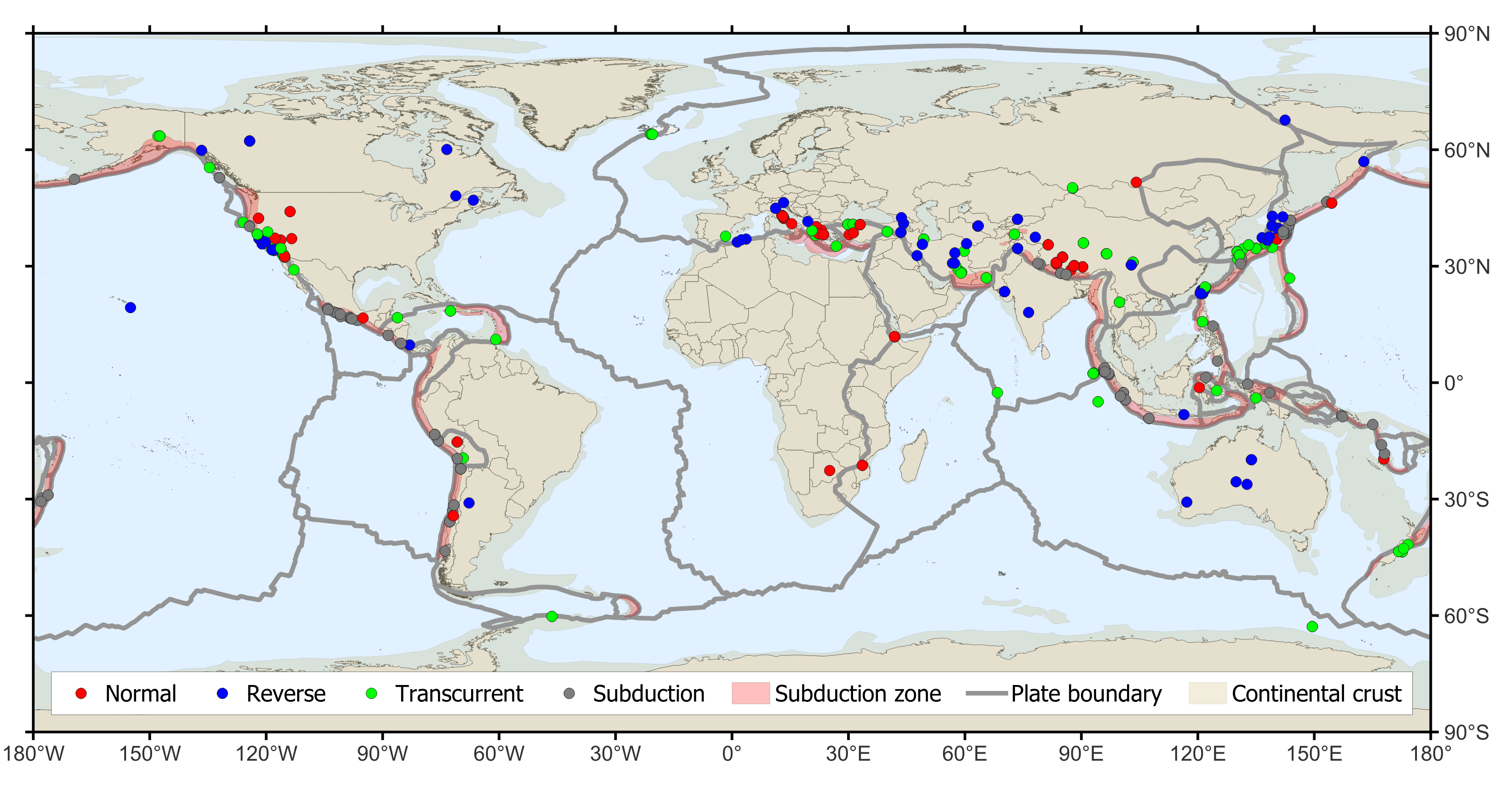
Map of the G-DIP dataset.
- Details
- Category: datasets
- Details
- Category: datasets
Users can address mail related to the content of this dataset to the following persons:
Project SHARE Work Package 3: Gianluca Valensise, email:
Task 3.2 and database content: Roberto Basili, email:
Database functionalities and website: Gabriele Tarabusi, email:
OGC web services: Roberto Vallone, email:
Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia
Via di Vigna Murata, 605
00143 Roma, Italy
- Details
- Category: datasets
The European Database of Seismogenic Faults (EDSF) was designed as a "work in progress" and, as such, it is open to later additions and improvements. Due to its intrinsic nature, EDSF cannot be guaranteed to be complete, accurate, and updated in any part and will be subjected to successive revisions. Although we make every possible effort to supply the best available information, no warranty, expressed or implied, is provided regarding the accuracy and reliability of the data supplied in EDSF. Users are invited to consider the inherent epistemic uncertainty of such a database in earthquake-related hazard analyses (PSHA, PTHA, PFDHA). We recall that EDSF was designed for analyses at the scale of a continent (the Euro-Mediterranean region) and that it is thus necessary to add local and site-specific investigations when using EDSF data for studies at more local scales. Users are also cautioned to carefully consider the nature of EDSF content before using it for decisions concerning personal or public safety or in relation to business involving substantial financial or operational consequences.






